The Benefits of Spring Boot
Spring Boot makes it easy for developers to create standalone and production-ready Spring applications without requiring any separate configurations. Some key advantages of Spring Boot include:
Reduced boilerplate code: Spring Boot includes features that reduce the amount of code needed for common tasks like automatic bean configuration and code generation. This allows developers to focus more on business logic.
Easy standalone applications: Applications built with Spring Boot can run without the need for an external application server due to its embedded servlet container. This makes deployment much simpler.
Fast and easy setup: Starter dependencies allow developers to quickly add common functionalities like security, SQL/NoSQL databases with minimal code. For example, the spring-boot-starter-web dependency adds Tomcat and Spring MVC.
Improved testability: Features like test configuration and in-memory databases help make applications more testable during development.
Taking Advantage of Convention over Configuration
One of the main benefits of Spring Boot is that it favors convention over configuration, eliminating much of the redundant configuration code that comes with standard Spring applications. Spring Boot apps can be easily deployed as standalone jar files with all dependencies bundled inside. This drastically reduces the initial setup time compared to traditional Spring projects.

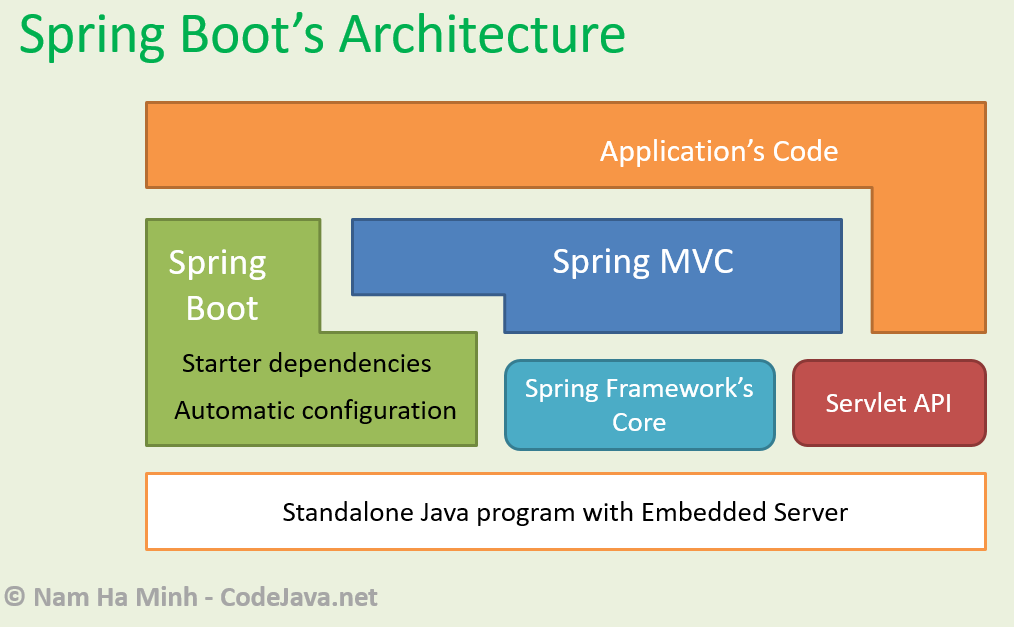
Understanding Spring MVC and Its Role
Spring MVC is a model-view-controller web framework that allows building web applications in a structured and efficient manner. Some key aspects of Spring MVC: Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern: Follows the MVC architectural pattern for separating application logic, presentation and user input handling. This improves testability and maintainability. Annotations-based: Configuration is done using annotations rather than XML which reduces boilerplate code. REST support: Provides out-of-the-box support for building RESTful web services. View resolution: Supports JSP, Thymeleaf and other templating engines for separating view definition from application code. Controllers: Handle user requests and responses. Controllers can directly access databases or call services. While Spring MVC provides a way to build web apps, it requires separate configurations. Spring Boot addresses this by providing preconfigured starter dependencies combining Spring MVC and embedded servers like Tomcat.
Integrating Databases Seamlessly
Spring Boot starters make it easy to connect and interact with databases. Starter dependencies like spring-boot-starter-data-jpa or spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb add common database dependencies and autoconfiguration for JPA/JDBC and MongoDB respectively. Developers can then simply configure database properties and implement repositories without dealing with lower level APIs. This simplifies app development significantly.
Bootstrapping a Basic Web App
Creating a basic web application with Spring Boot requires only a few steps:
- Add the
spring-boot-starter-webdependency to build a static web project with Tomcat - Develop a main application class annotated with
@SpringBootApplication - Create model, controller and view classes (e.g. using Thymeleaf)
- Configure database properties
- Run the application
Spring Boot will automatically carry out tasks like scanning components, configuration of in-memory database, embedding Tomcat etc. Developers can then focus on application logic instead of infrastructure configuration.
Rapid Prototyping with Automatic Configurations
The conventions based approach of Spring Boot enables rapid application prototyping. With basic bootstrapping in place, developers can immediately start coding without touching infrastructure configurations. This allows easily iterating on ideas and shifting focus to business logic. Models, controllers can be refactored or dropped in and Spring Boot will automatically reconfigure. This simplifies experimentation significantly over traditional Spring setups.
Spring Boot for Production-Grade Apps
While accelerating development, Spring Boot does not compromise on production readiness. Its starter dependencies combine relevant dependencies for tasks like security, monitoring etc. Some of the production features offered are: Metrics - Starter dependencies add Actuator module which exposes metrics like memory usage, request count over HTTP/JMX. Health Checks - Provides information on configuration properties and state of dependencies through HTTP health endpoint. Externalized Configuration - Supports external configuration properties from files, remote config servers. Logging - Autoconfigured logging allows setting log levels and log pattern from application properties file. Production-ready Features - Features like sensible defaults, auto-reconfiguration, self-starting allow direct deployment on cloud platforms. By making production readiness inherent, Spring Boot allows full focus on business logic during development while ensuring apps are actually production-hardened after deployment.
Conclusion
Spring Boot has revolutionized Spring development by automating configuration tasks and providing sensible defaults. Its convention-based approach allows focusing more on writing business logic while keeping applications production-ready. The combination of Spring MVC with embedded servers also simplifies web application development significantly compared to traditional Spring configuration. Overall, Spring Boot speeds up both development and deployment of production-grade JVM-based applications.
 How I Learned Programming and Cracked Codevita My First Time
How I Learned Programming and Cracked Codevita My First Time